Neurological disorders affect the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system. To identify these conditions accurately, doctors rely on advanced brain tests. These tests help detect abnormalities, assess brain function, and guide proper treatment. Below is a detailed guide to the most commonly used brain tests for diagnosing neurological disorders.
What Are Brain Tests?
Brain tests are medical diagnostic procedures used to evaluate:
- Brain activity
- Cognitive function
- Nerve signals
- Blood flow to the brain
Doctors recommend brain tests when patients show symptoms related to neurological disorders.
Why Brain Tests Are Important in Neurology
Brain tests help doctors to:
- Detect neurological diseases early
- Identify the cause of symptoms
- Monitor disease progression
- Plan effective treatment
- Prevent long-term complications
Early diagnosis improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Common Symptoms That Require Brain Tests
Doctors may suggest brain tests if a patient experiences:
- Persistent headaches or migraines
- Seizures or fainting episodes
- Memory loss or confusion
- Difficulty in speech or movement
- Sudden weakness or numbness
- Head injury or trauma
- Vision or balance problems
Top Brain Tests Used to Diagnose Neurological Disorders
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
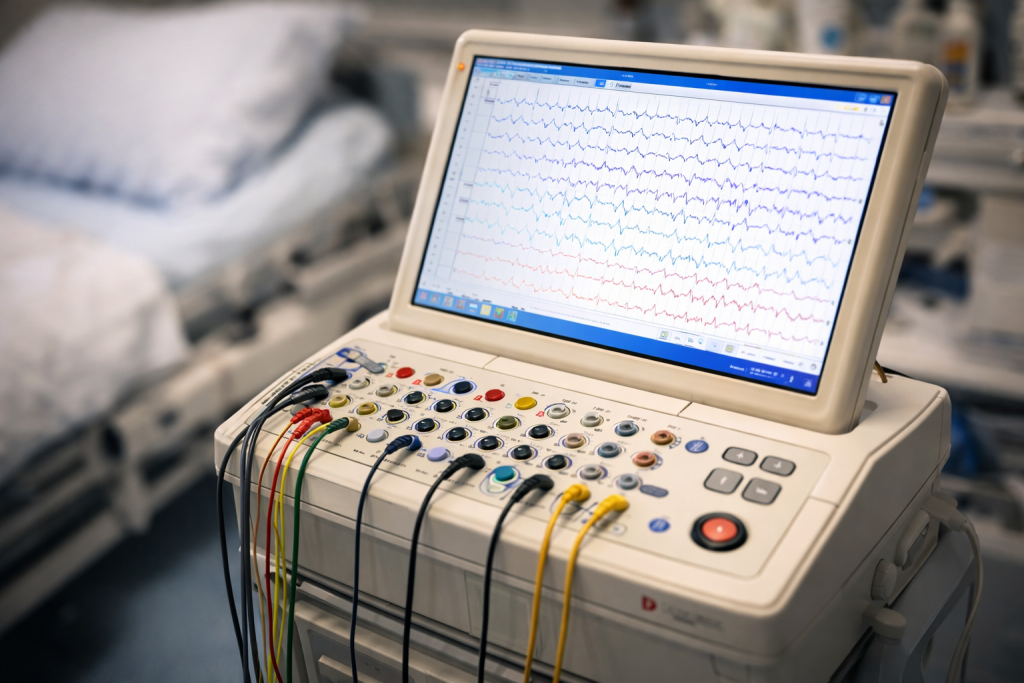
EEG is one of the most widely used brain tests.
Purpose of EEG:
- Measures electrical activity of the brain
- Detects abnormal brain waves
Common conditions diagnosed using EEG:
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Sleep disorders
- Brain infections
- Brain tumors
- Altered consciousness
Key benefits:
- Non-invasive
- Painless procedure
- Safe for all age groups
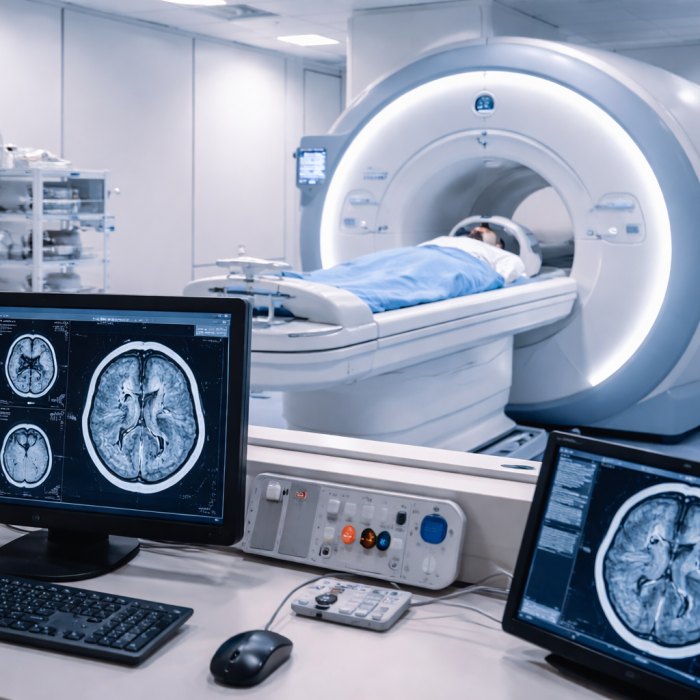
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Brain Scan
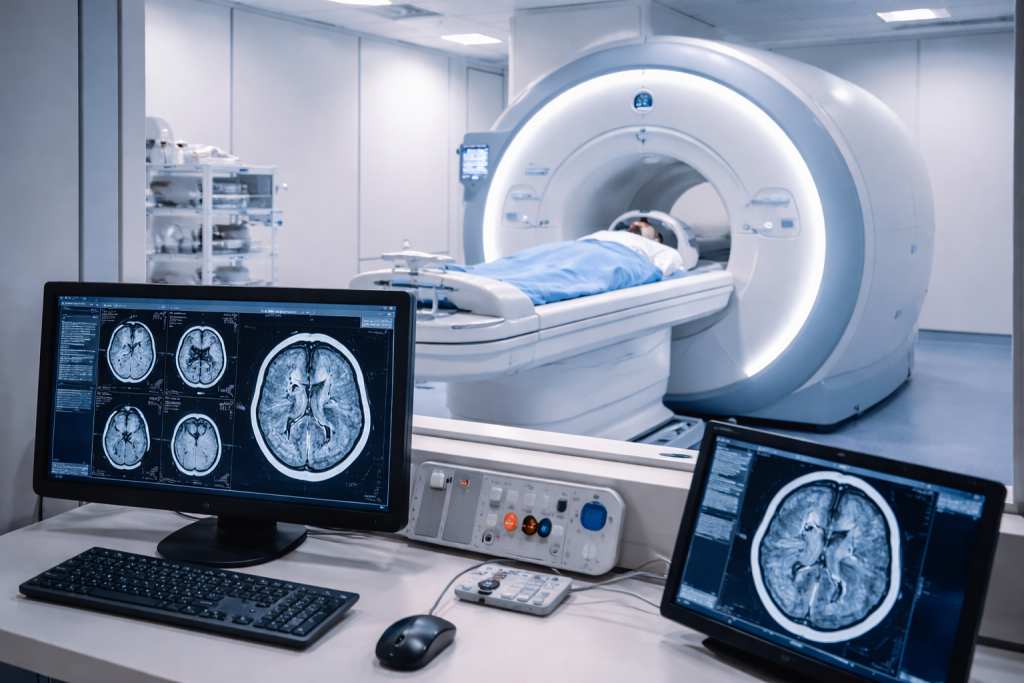
MRI provides detailed images of brain structures.
Purpose of MRI brain test:
- Identifies structural abnormalities
- Detects soft tissue damage
Conditions diagnosed using MRI:
- Brain tumors
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain infections
- Degenerative brain disorders
Why MRI is preferred:
- High-resolution images
- No radiation exposure
- Accurate diagnosis
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan of the Brain
CT scan is often used in emergency cases.
Purpose of CT scan:
- Detects bleeding or swelling
- Identifies fractures and injuries
Conditions diagnosed using CT scan:
- Brain hemorrhage
- Head trauma
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Hydrocephalus
Advantages:
- Fast results
- Useful in critical situations
- Widely available
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
PET scan evaluates brain metabolism and function.
Purpose of PET scan:
- Measures brain activity
- Detects abnormal cell function
Conditions diagnosed using PET scan:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Brain tumors
- Epilepsy
- Dementia
Key benefits:
- Functional brain imaging
- Early disease detection
- Helps in treatment planning
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
SPECT measures blood flow to different areas of the brain.
Purpose of SPECT scan:
- Evaluates brain circulation
- Identifies functional abnormalities
Common uses:
- Epilepsy evaluation
- Stroke diagnosis
- Brain injury assessment
- Dementia evaluation
Neuropsychological Brain Tests
These tests assess cognitive and mental functions.
Purpose of neuropsychological testing:
- Measures memory and attention
- Evaluates problem-solving skills
Conditions diagnosed:
- Dementia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Learning disorders
- Brain injury effects
- Mental health conditions
Assessment areas include:
- Memory
- Language
- Concentration
- Decision-making
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies
These tests assess nerve and muscle function.
Purpose of EMG and NCS:
- Detect nerve damage
- Measure muscle response
Conditions diagnosed:
- Neuropathy
- Motor neuron disease
- Muscle disorders
- Nerve compression
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
This test analyzes cerebrospinal fluid.
Purpose of lumbar puncture:
- Detects infections and inflammation
- Measures pressure around the brain
Conditions diagnosed:
- Meningitis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain infections
- Autoimmune disorders
Brain Blood Tests (Supporting Diagnosis)
While not direct brain tests, blood tests help neurological diagnosis.
Purpose of neurological blood tests:
- Identify infections
- Detect autoimmune markers
Assess metabolic disorders
How Doctors Choose the Right Brain Test
Doctors decide based on:
- Patient symptoms
- Medical history
- Age and health condition
- Urgency of diagnosis
- Suspected neurological disorder
Often, multiple brain tests are combined for accurate results.
Are Brain Tests Safe?
Most brain tests are:
- Non-invasive
- Painless
- Medically approved
- Conducted under expert supervision
Imaging tests are performed following strict safety guidelines.
When Should You Consult a Neurologist?
Consult a neurologist if you notice:
- Sudden neurological symptoms
- Progressive memory loss
- Recurrent seizures
- Chronic headaches
- Difficulty in movement or speech
Early evaluation leads to better treatment outcomes.
Brain tests play a vital role in diagnosing neurological disorders. From EEG and MRI to advanced imaging like PET scans, each test provides valuable information about brain health. Accurate diagnosis helps doctors plan effective treatment and improve patient recovery.
If you or your loved ones experience neurological symptoms, timely brain testing can make a significant difference.